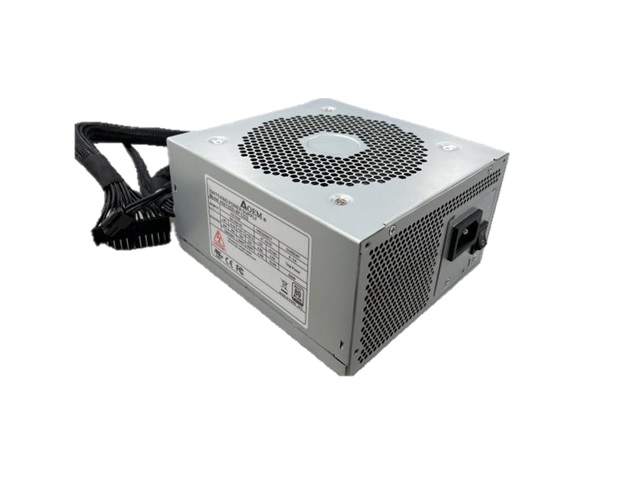
What is an AC-DC Power Supply?
AC-DC Power Supply Introduction
гЂЂгЂЂThe primary function of an AC-DC power supply is to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In our daily lives, most electronic devices require both forms of electricity. For example, cars run on 12V DC, while homes and businesses are powered by AC. Sometimes, we need to convert AC to DC, making AC-DC power supplies essential.How Does an AC-DC Power Supply Work?
гЂЂгЂЂAC-DC power supplies play a crucial role in modern electronic devices. They come in various forms, such as external transformers (like laptop adapters) and internal power converters (found in DVD players and medical equipment). Their basic working principles include transformers, rectifiers, and filters.- Transformer: A passive electrical device used to adjust voltage to meet device requirements.
- Rectifier: Converts AC to DC.
- Filter: Eliminates “noise” in the current, ensuring stable power output.
What Happens If You Don’t Use an AC-DC Power Supply?
гЂЂгЂЂFor devices that require DC, using AC directly can cause damage, potentially leading to fires or explosions. Incorrect power supply can also pose life-threatening risks. Therefore, using the correct power supply as per device requirements is crucial.Why Are There Two Types of Electricity?
гЂЂгЂЂThe choice of electricity types dates back to the late 19th century competition between Tesla and Edison. AC is suitable for long-distance transmission, while DC provides more stable power. Although AC dominates the power grid, many household and commercial devices still require DC, necessitating AC-DC power supplies for conversion.Differences Between AC and DC
- Alternating Current (AC): The standard power supplied to homes and businesses, where the current periodically changes direction and amplitude. AC voltage and frequency vary by region, e.g., 120V and 60Hz in the US, 230V and 50Hz in the UK. Due to its high transmission efficiency, AC is the preferred choice for global power grids.
- Direct Current (DC): The current flows in a single direction, commonly found in batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells. DC provides stable voltage but is not suitable for long-distance transmission. Since electronic devices require stable power, most use DC, necessitating AC-DC power supplies for conversion.
Types of AC-DC Power Supplies
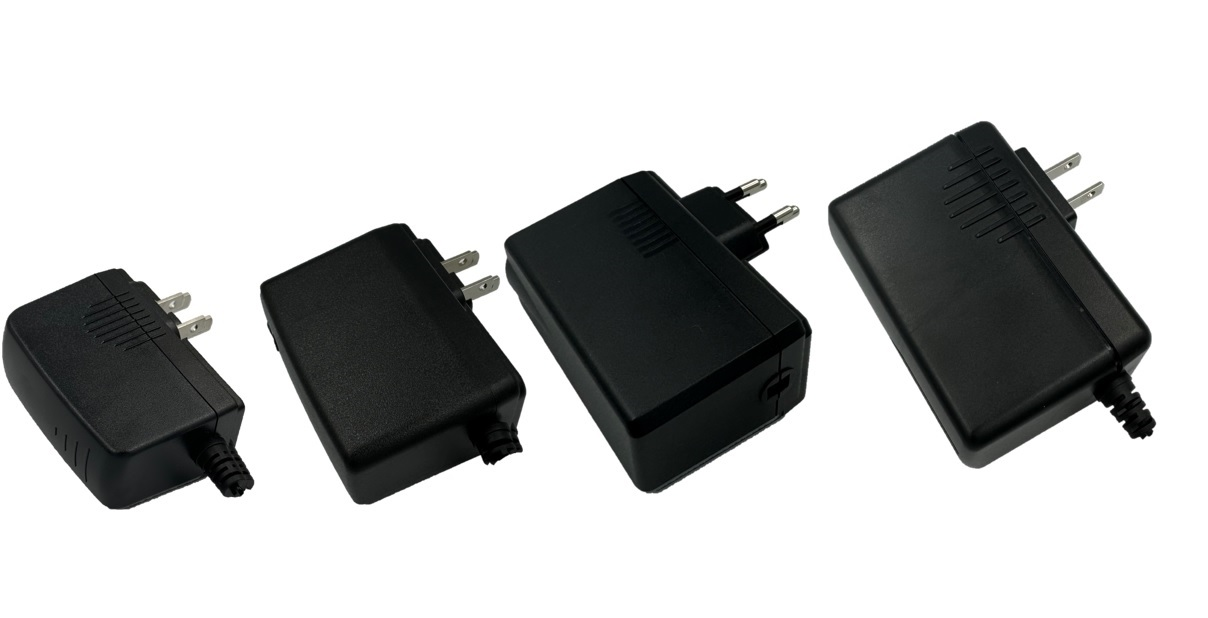
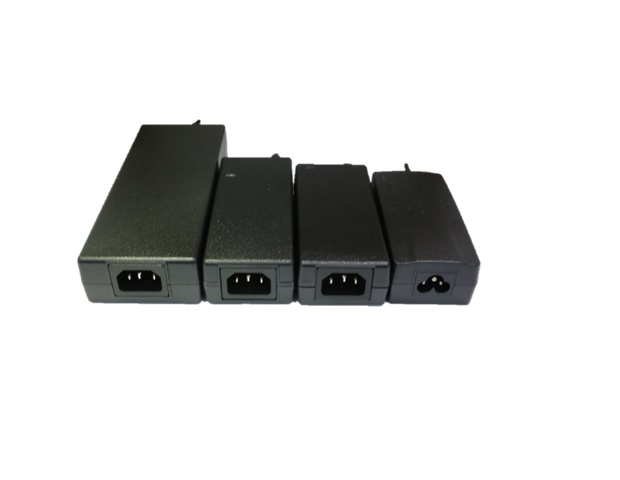
гЂЂгЂЂThere are various AC-DC power supplies available to meet different needs:- Adapter-Type AC-DC Power Supplies: These are usually compact and suitable for household and commercial electronic products like laptops and TVs. They offer output power ranging from 10W to 330W and voltage from 5V to 54V, complying with DoE Level VI standards.
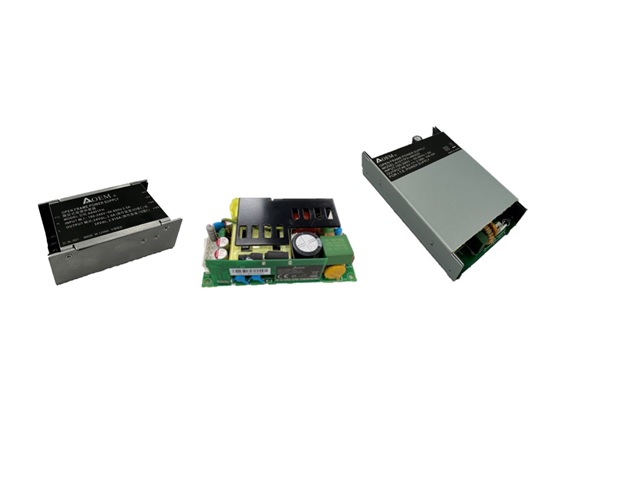
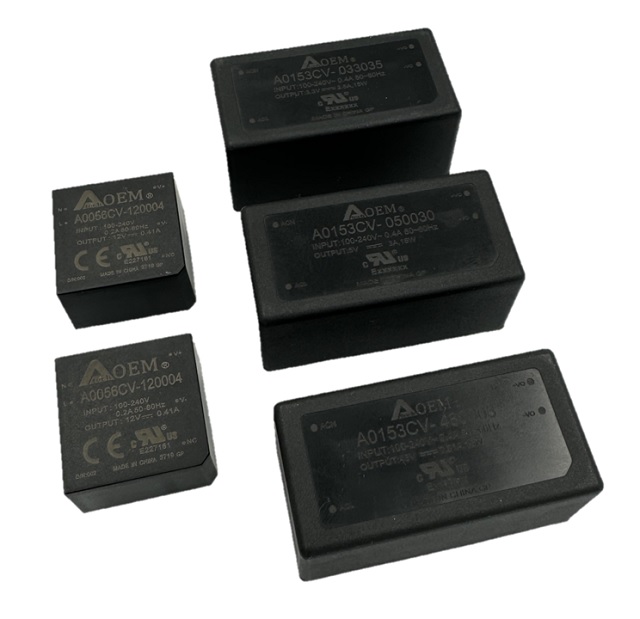
- Board-Mounted Power Supplies: These are installed on circuit boards without protective casings. They can be customized to meet different size and power requirements, offering options from 30W to 520W and supporting output voltages from 5V to 54V.
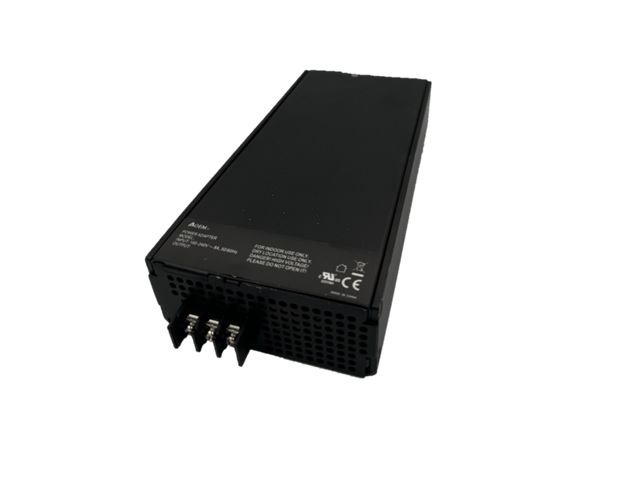
- Industrial Computer Power Supplies: Designed for industrial environments, providing high power and reliability. These power supplies comply with IEC 62368 and IEC 60950 standards, suitable for extreme environments, and offer high energy efficiency. They range from 450W to 850W, supporting various input voltages.
How to Choose an AC-DC Power Supply?
гЂЂгЂЂWhen selecting an AC-DC power supply, consider the following points:- Requirements: Choose based on the device’s performance needs and budget. For example, processors require high-power power supplies.
- Features: Select the necessary protection features, such as overload protection and overheat protection.
- Power: Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient power, ideally slightly higher than the device’s requirements.
- Efficiency: Choose high-efficiency power supplies, such as 80 PLUS Gold or Platinum, to reduce energy waste and heat.
- Brand: Opt for reputable brands to ensure product quality and reliability. AAEON has extensive experience in power supplies, offering a variety of products and excellent customer service.